
Which processes can be automated with RPA? Consequently, companies are faced with the central question of which processes can be automated sensibly and effectively without the automation bringing new – and perhaps even serious – problems with it. In addition, not every process is suitable for automation using RPA.
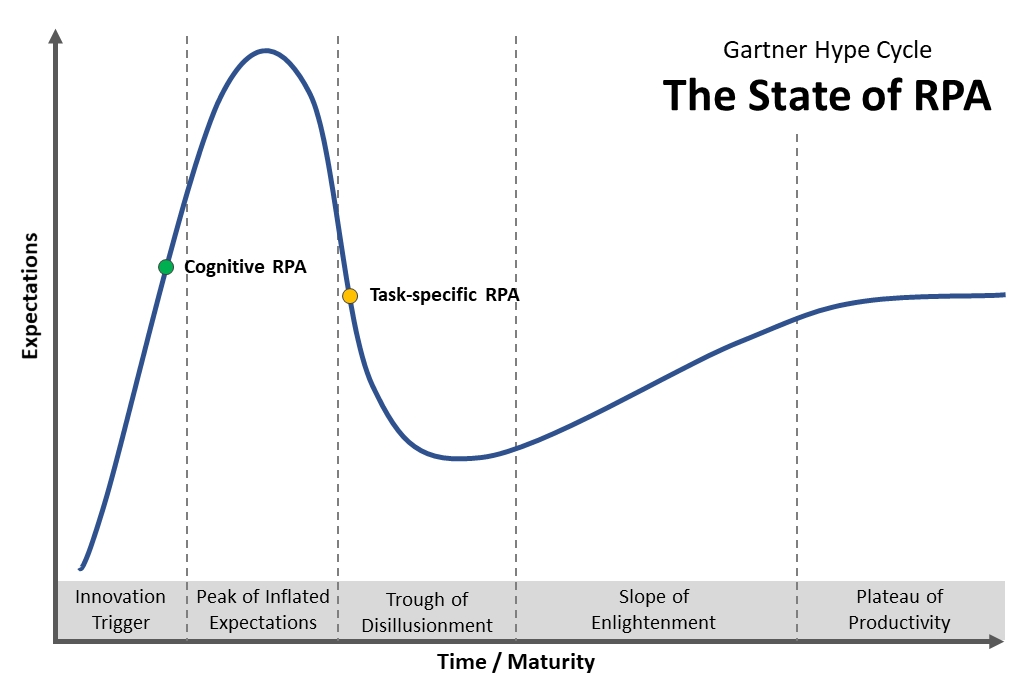
#Gartner hype cycle rpa software
The chances of successful and stable execution of software robots can be increased in this way, but, contrary to the promises of many RPA vendors, requires greater technical expertise. The latter can be ensured by using provided components within an RPA configuration software. Therefore, increased use of technologies such as Artificial Intelligence and Optical Character Recognition (OCR) and a shift away from pure front-end to increased back-end integration can be observed. It is thus apparent that the methods for recording and modeling processes are not yet fully mature. Automation is still possible, but it often requires a great deal of maintenance, which can suddenly turn what was initially a low-cost integration into an expensive undertaking. In times of constant updates and visual adjustments, this is a major problem. In particular, the stability of the performance of the software robots is a major shortcoming in many cases: Even the smallest changes to the user interface – for example, moving a button – can cause a robot to fail. To portray a holistic picture of RPA, however, the disadvantages of the technology must also be taken into account. These are just some of the benefits of using RPA. Reducing the workload of employees also often creates increased satisfaction, as humans can invest their time in more challenging and exciting tasks. This can result in time savings, which in turn brings increased efficiency and increased productivity to an organization.
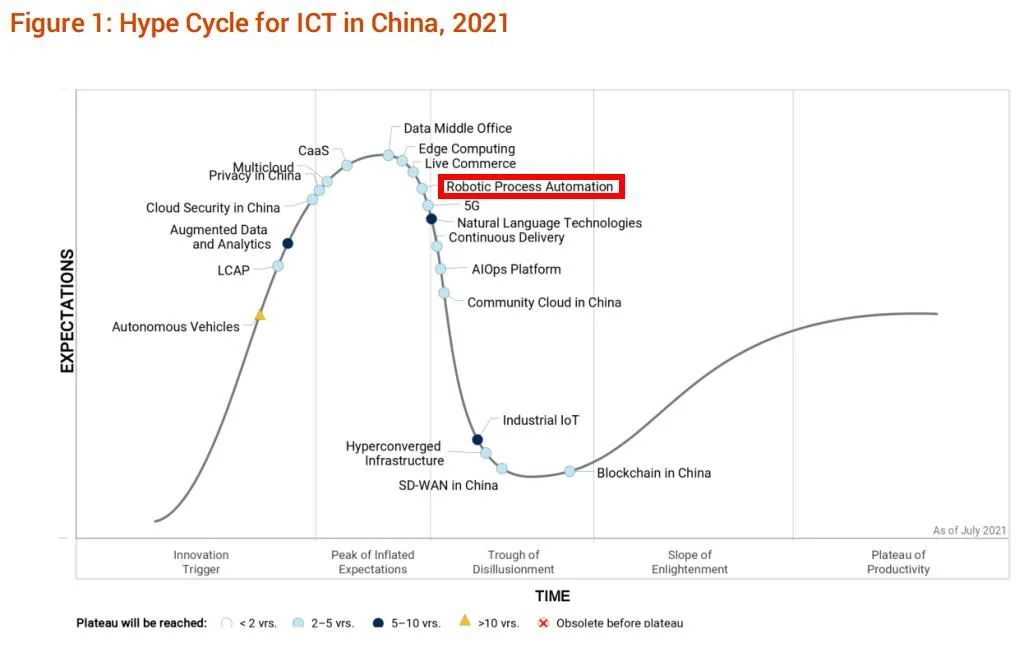
In addition, the speed of work can be significantly increased by using RPA robots. If procedures are always executed in the same way in a structured manner, there are no careless errors that can otherwise be caused by human carelessness. Another important aspect of automation is the quality of the work that is to be automated. The required technical know-how is therefore relatively low. RPA does not require any programming skills and is largely based on low-code implementations. Also not to be underestimated is the low development effort. This non-invasive characteristic of the technology also ensures trouble-free integration into the existing IT infrastructure, since different systems do not interfere with each other. Consequently, automation projects can be implemented quickly and cost-effectively with RPA. It is not necessary to redesign used information systems and existing business structures for the use of software robots. Automation technology brings with it many advantages. It is not without reason that RPA has become an important topic in a very short time. RPA solutions can run on individual desktop PCs as well as on corporate servers. Thus, the use of RPA does not require any changes to existing information systems, since a software robot works in a comparable way on the user interface as a human would. The process steps required for this are first recorded, modeled with the help of RPA tools or programmed in the form of scripts. More specifically, RPA uses software robots.The result is that processes that previously involved human interaction with user interfaces of various application programs are imitated by software robots and thus run automatically. For further information, see Guiding Principles on Independence and Objectivity.Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is one of the latest buzzwords, but what exactly does it mean? As the name suggests, it is a technology for automating processes. Its research is produced independently by its research organization without input or influence from any third party. Gartner prides itself on its reputation for independence and objectivity. Your access and use of this publication are governed by Gartner’s Usage Policy. Although Gartner research may address legal and financial issues, Gartner does not provide legal or investment advice and its research should not be construed or used as such. While the information contained in this publication has been obtained from sources believed to be reliable, Gartner disclaims all warranties as to the accuracy, completeness or adequacy of such information. It consists of the opinions of Gartner’s research organization, which should not be construed as statements of fact. This publication may not be reproduced or distributed in any form without Gartner’s prior written permission. Gartner is a registered trademark of Gartner, Inc.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
